Honeywell Quantum Solutions took part of the center stage at Microsoft’s Ignite conference on Monday when Microsoft announced a new service called “Azure Quantum.” Azure Quantum will provide internet cloud access to Honeywell’s quantum computer along with those of IonQ and QCI. The service also includes access to Microsoft's open-source Quantum Development Kit and a quantum simulator. At present, Microsoft has a classical computer on Azure, but it does not have quantum hardware available.
Until now, Honeywell was relatively silent about its quantum research. But I learned a long time ago that silence isn't an indication of how much work is being done.
For example, many years ago, I had a meeting scheduled with a few researchers at Bell Labs in Murray Hill, New Jersey. When I walked into the conference room, a few of the researchers looked like they were nodding off, and the others were staring into space. To an average person, it might have appeared these people were disinterested or perhaps even disconnected from the task. But from my experience working with Bell Labs, I knew what was going on. Despite appearances, they were all working, and probably very hard.
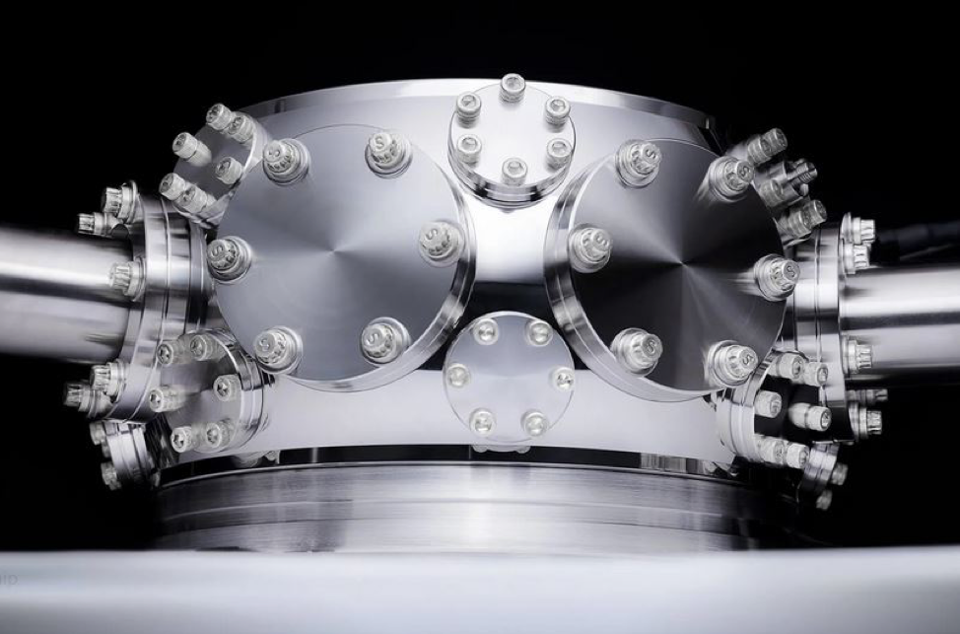
Based on Microsoft’s announcement, one thing is for sure: Honeywell has been hard at work. While the big techs, IBM, Google and Intel, use superconducting qubits, trapped ion is Honeywell’s technology of choice—for several reasons aside from the technical advantages it offers.
One reason is that Honeywell gained prior experience with the technology when it previously worked on a trapped ion program with Intelligence Advanced Research Projects Activity (IARPA) in 2014. Another factor is that Honeywell has the expertise and a long history of producing successful products and services using the same technology necessary to build a quantum computer. These include state-of-the-art hardware and software control systems, advanced electronics, photonics, lasers, modulators, fiber optics, ultra-high vacuum environments and cryogenics.
Honeywell has put their experience and expertise to work. It fabricates one of the most critical components, the ion trap, in its microfabrication production facility in Minneapolis. It also makes its own control system and user interfaces.
Last week, Patrick Moorhead, President and founder of Moor Insights and Strategy, and I had the opportunity to talk to Tony Uttley, President of Honeywell Quantum Solutions (HQS). For the reasons above, Uttley believes that quantum is a logical extension of the company's decades-long legacy in control systems.
He is also realistic about the future timelines of quantum computing. "I think of three eras," says Uttley. "The first era is when quantum computers and classical computers work together to solve problems.” He went on to define the next era as one he calls "classically impractical." According to him, that will be a time when some things are feasible on a classical computer but, because of speedup considerations, a quantum computer might be a better choice. Lastly, he defines the final era as "classically impossible." That’s when quantum computing becomes a mature technology and some computations can be done on a quantum computer that are impossible on a classical computer. Others have referred to this as the era of fault-tolerant quantum gate computers.
We asked Uttley about the number of qubits in Honeywell’s most current quantum computer, and how many were on the horizon. Uttley correctly answered that while the number of qubits is important, many other technical factors are equally important to the performance of a quantum computer.
It was clear that Uttley subscribes to the importance of IBM’s Quantum Volume, a method introduced in 2017 that evaluates key performance elements of a quantum computer. The three primary metrics that govern a quantum computer's QV are how many qubits the quantum computer has, how connected the qubits are (can every qubit easily interact with every other qubit?) and how many operations it can perform before too many errors occur or before the quantum states collapse.
We believe Honeywell's first quantum computer will have a relatively small number of qubits compared to IBM or Google. However, we also expect it to scale up in a reasonable amount of time. Keep an eye on Honeywell Quantum Solutions. Considering Honeywell’s history, expertise and financial strength, it will likely become a significant player.