Since its inception in 2008, Google Cloud has emerged as a key player in data cloud computing, delivering services to businesses across various industries and accommodating organizations ranging from small startups to large corporations. Much of Google Cloud’s growth and success can be attributed to its continuous innovations in-house, enhanced by technology brought in through key acquisitions.
Last month, I published an article on Google Data Cloud. In this piece, I build off the elements from that article to investigate the significance of generative AI within Google Cloud’s portfolio and enterprise strategy.
Google’s Acquisitions in AI, Cloud, and Beyond
It’s helpful to review some of the key investments that have helped Google Cloud reach its current state in AI and related technologies. In 2014, Google acquired DeepMind, which focuses on developing AI technology. It then acquired Apigee in 2016 to improve its API management services. The 2019 purchase of Cloud Foundry, an open-source PaaS, furthered the company’s cloud application development and management tools.
Kaggle, acquired in 2020, connected Google Cloud to a community of data scientists and added a platform for data science competitions. That same year, Google Cloud purchased Looker, expanding its business intelligence and data analytics capabilities. Siemplify, acquired in 2021, augmented Google Cloud’s cybersecurity services. The acquisition of Anthos Capital in 2022 provided access to innovative cloud-native startups, while Mandiant expanded Google’s security offerings in 2023. These strategic acquisitions have broadened Google’s services, attracted a broader enterprise customer base, and solidified Google Cloud’s place alongside its larger competitors AWS and Azure.
Google Enters Its GAI Renaissance
In 2017, Google extended its AI journey by launching a large language model (LLM) that analyzes how words in sentences influence each other. The journey progressed in 2018 with the debut of Bert, an LLM meant to understand human language and predict words. This was followed by the release of the T5 model in 2019, which focused on predicting missing text segments. (If you’re looking for a tongue-twister, try the full name of T5: Text-To-Text Transfer Transformer.) In 2020, Google introduced LaMDA, a conversational LLM. The next advancement came in 2021 with AlphaFold, an LLM specializing in prediction. In 2022, Google launched Palm, a multifunctional LLM; in 2023, it unveiled Bard, a chat-based AI tool powered by LaMDA.
Google AI Expands with Duet AI
As I shift the discussion toward Google products, I want to bring attention to some pieces by my Moor Insights & Strategy colleagues that shed light on Google’s progress in generative AI. One, by vice president and principal analyst Melody Brue, addresses Google’s collaborative workspace. Another, by chief analyst and CEO Patrick Moorhead, explores Google’s support for generative AI.
Duet AI, an AI-powered collaboration tool, is designed to improve productivity and efficiency in Google Cloud or applications such as Google Workspace. It’s currently available to Google Workspace, for developers, and in Chronicle Security Operations, with general availability coming in February 2024. Its features include code assistance, chat support, automated document creation, and log summarization for debugging. In office settings, Duet AI helps refine emails, create project plans, generate images, and summarize meetings. Its integration into Chronicle Security Operations aids in analyzing and resolving security threats by collecting and examining data and using generative AI for assistance. This integration aims to save time and improve efficiency in handling large data sets and security incidents.
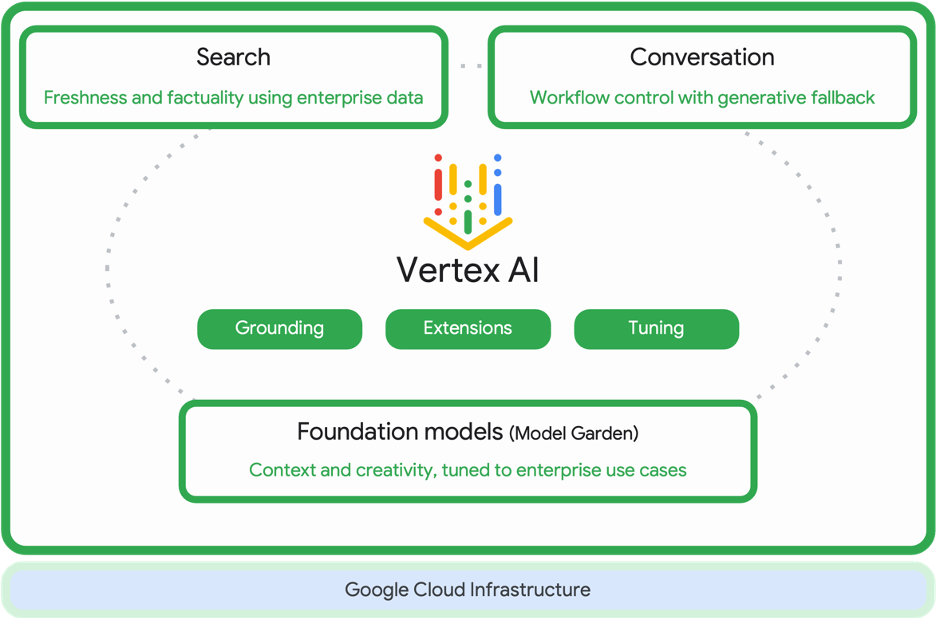
Vertex AI is a platform for training and deploying AI and ML models. It also allows users to customize LLMs for their AI-powered applications. The image above shows the Vertex AI workflow, which is designed to help businesses build, deploy, and manage ML models at scale. Google Cloud’s strategy gives businesses increased control and flexibility in utilizing generative AI. This approach is designed to assist enterprises in quickly finding important information, discovering insights in their data, and improving productivity for customers, employees, and other stakeholders.
Alongside Vertex AI, Google has introduced Model Garden, a versatile platform where enterprises can choose models that best suit their specific needs. Model Garden offers a variety of options (127 models, at the time of writing) ranging from Google’s in-house models such as PaLM, Imagen, Codey, and Chirp to pre-trained APIs in areas such as speech-to-text, natural language processing, translation, and vision. Additionally, it includes open-source models such as Meta’s Llama 2 and TII’s Falcon and integrates with third-party models such as Anthropic’s Claude 2.
These improvements focus on simplifying the customization and augmentation of models according to a company’s specific data. This allows businesses to choose and use the most suitable models for their needs, considering factors like functionality, size, and the ability to customize. The goal is to provide advanced AI tools and the flexibility required for effective and large-scale implementation.
Vertex AI: Enterprise-Ready GAI
Vertex AI is ready for enterprise use, allowing customers to harness its capabilities to analyze large datasets, gain insights, enhance decision-making, and improve customer experiences. Vertex AI simplifies the AI implementation process, making it more accessible to businesses without requiring deep technical expertise in machine learning. Vertex AI is also built to meet enterprises’ needs by providing data governance, indemnity, and privacy guarantees; security and compliance features; highly reliable and sustainable infrastructure; and tooling for safety and responsible AI.
Here are a few examples demonstrating how Vertex AI could be used in the field.
- Retail — Vertex AI trains a model to forecast product demand, helping optimize inventory and enhance customer satisfaction.
- Financial Services — A company uses Vertex AI to develop a model that detects potentially suspicious transactions and mitigates risks.
- Healthcare — A company can leverage Vertex AI to develop a model for diagnosing diseases, aiming to enhance the precision and speed of medical diagnoses.

Google Expands Its AI Portfolio with Gemini
Google’s AI journey has now led it to the release of Gemini, the next-generation successor to PaLM. What’s groundbreaking about Gemini is its multimodality—it reasons across text, images, video, audio, and code. Gemini is the first model to outperform human experts on MMLU (Massive Multitask Language Understanding), one of the most popular methods to test AI models’ knowledge and problem-solving abilities. Gemini foundational models come in three sizes: Ultra for the largest and most complex tasks, Pro for the best performance for a broad range of functions, and Nano for on-device tasks. Users can explore Gemini through a web interface in Vertex AI, and developers have access to Gemini Pro via Google’s newly announced AI Studio, a web-based environment for developing LLMs with APIs. Gemini should bring efficiency to API integrations, allowing less intensive integration of systems and applications.
Let’s explore a few potential Gemini use cases in different fields.
- Programming — Gemini can generate complete programs from natural language descriptions and automate repetitive coding tasks.
- Cloud and Edge Computing — Gemini can predict resource usage to improve efficiency and performance. It can also diagnose and analyze system logs for problem identification.
- Sales and Marketing — Gemini can tailor sales and marketing efforts, including emails, targeted campaigns, and customer service.
- Virtual Assistants — Gemini’s enhanced conversational ability allows it to understand and respond to users more effectively, interacting through various modalities such as text, images, video, and code.
- Wearable Technology — Gemini can contribute to more intelligent, responsive devices by providing relevant data and insights. For example, proactive health devices could offer personalized suggestions.
- Google Products and Services — Expect Gemini to be integrated into various Google domains, such as Bard, Maps, Docs, Translate, and others.
Gemini will be available in the Vertex AI Model Garden for enterprise customers and to developers and hobbyists via the Gemini API in the Google AI Studio. Another place to try Gemini Pro is in Bard, where you can test it against its main competitor, ChatGPT. Google testing reports that Gemini Pro performed better than GPT-3.5 and comparably to GPT-4, but time will tell how well that holds up in the real world.
Gemini’s Competition
In the competitive field of LLMs, success depends on several factors: investment in research and development; access to diverse data sets for training; outright performance; and the model’s specific focus, for example accuracy or creativity. Despite Gemini’s potential, it operates in a rapidly evolving landscape where models continuously improve. LLMs’ future will likely continue to involve both competition and collaboration driving innovation.
Gemini’s immediate competitor is Open AI’s ChatGPT, which has similar capabilities across text generation, question and answer, and translation. ChatGPT is recognized for its ability to generate human-like text, having been trained on a large amount of data, while Gemini offers multimodal functionalities. Microsoft’s Megatron-Turing natural language generation (NLG) has text generation and language modeling capabilities; although it is not as well known as ChatGPT, it has the potential to compete with Gemini. Another notable competitor is Anthropic’s Claude 2 LLM, which is known for its focus on safety and interpretability, making it a potentially strong competitor in ethically oriented sectors. Meta’s Blender, for its creative writing capabilities, is a potential competitor in creative text-generation tasks.
Wrap-Up
Google’s approach to AI development has been characterized by progress on internal projects such as Google Research and DeepMind, complemented by strategic acquisitions. These steps have brought Google a range of innovative technologies from data and cloud startups that have enhanced its portfolio with products such as Gemini, Vertex AI, and Duet AI. Collectively, Google’s strategy of acquisitions and development in AI technology demonstrates its dedication to evolving AI applications across diverse sectors.
Gemini is particularly notable for its multimodal abilities and performance on complex tasks, such as math and physics, along with its MMLU performance. I’m interested to see if the buzz around Gemini translates into practical use cases and real-world feedback.
Vertex AI’s expansion enhances Google’s influence in numerous industries, especially healthcare, as it brings fresh models including MedLM to the Model Garden. Meanwhile, Duet AI is set to be incorporated into additional Google Cloud offerings, including BigQuery, Looker, Google’s portfolio of database offerings, and Apigee.
Over the years, Google has done a lot to improve the generative AI capabilities within its enterprise data cloud services. These improvements mean that Google’s enterprise data cloud can now better serve a wide range of business needs, making it a strong option for companies seeking reliable, scalable, and secure cloud solutions, particularly in the area of generative AI.